Python Things
Table of Contents
Awesome
parse argument
http://docs.python.org/2/library/argparse.html
import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Process some integers.') parser.add_argument('integers', metavar='N', type=int, nargs='+', help='an integer for the accumulator') parser.add_argument('--sum', dest='accumulate', action='store_const', const=sum, default=max, help='sum the integers (default: find the max)') args = parser.parse_args() print args.accumulate(args.integers)
$ prog.py 1 2 3 4 4 $ prog.py 1 2 3 4 --sum 10
Configuration file parser
pySerial
sudo apt-get install python-pip pip install mechanize pip install pyserial
IDE
IDLE
IDLE is an integrated development environment for Python.
Anaconda
Anaconda is a free and open-source distribution of the Python and R programming languages for scientific computing,
PyCharm
PyCharm is an integrated development environment used in computer programming, specifically for the Python language.
python Ping
A pure python ping implementation using raw socket.
http://www.g-loaded.eu/2009/10/30/python-ping/
#!/usr/bin/env python """ A pure python ping implementation using raw socket. Note that ICMP messages can only be sent from processes running as root. Derived from ping.c distributed in Linux's netkit. That code is copyright (c) 1989 by The Regents of the University of California. That code is in turn derived from code written by Mike Muuss of the US Army Ballistic Research Laboratory in December, 1983 and placed in the public domain. They have my thanks. Bugs are naturally mine. I'd be glad to hear about them. There are certainly word - size dependenceies here. Copyright (c) Matthew Dixon Cowles, <http://www.visi.com/~mdc/>. Distributable under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2. Provided with no warranties of any sort. Original Version from Matthew Dixon Cowles: -> ftp://ftp.visi.com/users/mdc/ping.py Rewrite by Jens Diemer: -> http://www.python-forum.de/post-69122.html#69122 Rewrite by George Notaras: -> http://www.g-loaded.eu/2009/10/30/python-ping/ Revision history ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ November 8, 2009 ---------------- Improved compatibility with GNU/Linux systems. Fixes by: * George Notaras -- http://www.g-loaded.eu Reported by: * Chris Hallman -- http://cdhallman.blogspot.com Changes in this release: - Re-use time.time() instead of time.clock(). The 2007 implementation worked only under Microsoft Windows. Failed on GNU/Linux. time.clock() behaves differently under the two OSes[1]. [1] http://docs.python.org/library/time.html#time.clock May 30, 2007 ------------ little rewrite by Jens Diemer: - change socket asterisk import to a normal import - replace time.time() with time.clock() - delete "return None" (or change to "return" only) - in checksum() rename "str" to "source_string" November 22, 1997 ----------------- Initial hack. Doesn't do much, but rather than try to guess what features I (or others) will want in the future, I've only put in what I need now. December 16, 1997 ----------------- For some reason, the checksum bytes are in the wrong order when this is run under Solaris 2.X for SPARC but it works right under Linux x86. Since I don't know just what's wrong, I'll swap the bytes always and then do an htons(). December 4, 2000 ---------------- Changed the struct.pack() calls to pack the checksum and ID as unsigned. My thanks to Jerome Poincheval for the fix. Last commit info: ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ $LastChangedDate: $ $Rev: $ $Author: $ """ import os, sys, socket, struct, select, time # From /usr/include/linux/icmp.h; your milage may vary. ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST = 8 # Seems to be the same on Solaris. def checksum(source_string): """ I'm not too confident that this is right but testing seems to suggest that it gives the same answers as in_cksum in ping.c """ sum = 0 countTo = (len(source_string)/2)*2 count = 0 while count<countTo: thisVal = ord(source_string[count + 1])*256 + ord(source_string[count]) sum = sum + thisVal sum = sum & 0xffffffff # Necessary? count = count + 2 if countTo<len(source_string): sum = sum + ord(source_string[len(source_string) - 1]) sum = sum & 0xffffffff # Necessary? sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff) sum = sum + (sum >> 16) answer = ~sum answer = answer & 0xffff # Swap bytes. Bugger me if I know why. answer = answer >> 8 | (answer << 8 & 0xff00) return answer def receive_one_ping(my_socket, ID, timeout): """ receive the ping from the socket. """ timeLeft = timeout while True: startedSelect = time.time() whatReady = select.select([my_socket], [], [], timeLeft) howLongInSelect = (time.time() - startedSelect) if whatReady[0] == []: # Timeout return timeReceived = time.time() recPacket, addr = my_socket.recvfrom(1024) icmpHeader = recPacket[20:28] type, code, checksum, packetID, sequence = struct.unpack( "bbHHh", icmpHeader ) if packetID == ID: bytesInDouble = struct.calcsize("d") timeSent = struct.unpack("d", recPacket[28:28 + bytesInDouble])[0] return timeReceived - timeSent timeLeft = timeLeft - howLongInSelect if timeLeft <= 0: return def send_one_ping(my_socket, dest_addr, ID): """ Send one ping to the given >dest_addr<. """ dest_addr = socket.gethostbyname(dest_addr) # Header is type (8), code (8), checksum (16), id (16), sequence (16) my_checksum = 0 # Make a dummy heder with a 0 checksum. header = struct.pack("bbHHh", ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, my_checksum, ID, 1) bytesInDouble = struct.calcsize("d") data = (192 - bytesInDouble) * "Q" data = struct.pack("d", time.time()) + data # Calculate the checksum on the data and the dummy header. my_checksum = checksum(header + data) # Now that we have the right checksum, we put that in. It's just easier # to make up a new header than to stuff it into the dummy. header = struct.pack( "bbHHh", ICMP_ECHO_REQUEST, 0, socket.htons(my_checksum), ID, 1 ) packet = header + data my_socket.sendto(packet, (dest_addr, 1)) # Don't know about the 1 def do_one(dest_addr, timeout): """ Returns either the delay (in seconds) or none on timeout. """ icmp = socket.getprotobyname("icmp") try: my_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_RAW, icmp) except socket.error, (errno, msg): if errno == 1: # Operation not permitted msg = msg + ( " - Note that ICMP messages can only be sent from processes" " running as root." ) raise socket.error(msg) raise # raise the original error my_ID = os.getpid() & 0xFFFF send_one_ping(my_socket, dest_addr, my_ID) delay = receive_one_ping(my_socket, my_ID, timeout) my_socket.close() return delay def verbose_ping(dest_addr, timeout = 2, count = 4): """ Send >count< ping to >dest_addr< with the given >timeout< and display the result. """ for i in xrange(count): print "ping %s..." % dest_addr, try: delay = do_one(dest_addr, timeout) except socket.gaierror, e: print "failed. (socket error: '%s')" % e[1] break if delay == None: print "failed. (timeout within %ssec.)" % timeout else: delay = delay * 1000 print "get ping in %0.4fms" % delay print if __name__ == '__main__': verbose_ping("heise.de") verbose_ping("google.com") verbose_ping("a-test-url-taht-is-not-available.com") verbose_ping("192.168.1.1")
ping and traceroute
http://www.python.org/~jeremy/python.html
ping.tar.gz
Some simple-minded code for manipulating raw IP, ICMP, and UDP packets. They allow you to write ping and traceroute completely in Python; the code is smaller and simpler than the corresponding C versions (e.g. traceroute.c). The code was written for Python 1.4; it should be updated to use the new features of the struct module in 1.5.
A pure python ICMP ping implementation using raw sockets.
Lars Strand's ping
ping.py uses the ICMP protocol's mandatory ECHOREQUEST datagram to elicit an ICMP ECHORESPONSE from a host or gateway.
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: iso-8859-1 -*- """ping.py ping.py uses the ICMP protocol's mandatory ECHO_REQUEST datagram to elicit an ICMP ECHO_RESPONSE from a host or gateway. Copyright (C) 2004 - Lars Strand <lars strand at gnist org> This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA. Must be running as root, or write a suid-wrapper. Since newer *nix variants, the kernel ignores the set[ug]id flags on #! scripts for security reasons RFC792, echo/reply message: 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Type | Code | Checksum | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Identifier | Sequence Number | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Data ... +-+-+-+-+- TODO: - do not create socket inside 'while' (but if not: ipv6 won't work) - add support for broadcast/multicast - add support for own payload string CHANGELOG: DONE --> bugfix from Filip Van Raemdonck mechanix debian org DONE --> add more support for modules (raise instead of sys.exit) DONE --> locale func names DONE --> package def DONE --> some code cleanup """ import sys import os import struct import array import time import select import binascii import math import getopt import string import socket # total size of data (payload) ICMP_DATA_STR = 56 # initial values of header variables ICMP_TYPE = 8 ICMP_TYPE_IP6 = 128 ICMP_CODE = 0 ICMP_CHECKSUM = 0 ICMP_ID = 0 ICMP_SEQ_NR = 0 # Package definitions. __program__ = 'ping' __version__ = '0.5a' __date__ = '2004/15/12' __author__ = 'Lars Strand <lars at unik no>' __licence__ = 'GPL' __copyright__ = 'Copyright (C) 2004 Lars Strand' def _construct(id, size, ipv6): """Constructs a ICMP echo packet of variable size """ # size must be big enough to contain time sent if size < int(struct.calcsize("d")): _error("packetsize to small, must be at least %d" % int(struct.calcsize("d"))) # construct header if ipv6: header = struct.pack('BbHHh', ICMP_TYPE_IP6, ICMP_CODE, ICMP_CHECKSUM, ICMP_ID, ICMP_SEQ_NR+id) else: header = struct.pack('bbHHh', ICMP_TYPE, ICMP_CODE, ICMP_CHECKSUM, ICMP_ID, ICMP_SEQ_NR+id) # if size big enough, embed this payload load = "-- IF YOU ARE READING THIS YOU ARE A NERD! --" # space for time size -= struct.calcsize("d") # construct payload based on size, may be omitted :) rest = "" if size > len(load): rest = load size -= len(load) # pad the rest of payload rest += size * "X" # pack data = struct.pack("d", time.time()) + rest packet = header + data # ping packet without checksum checksum = _in_cksum(packet) # make checksum # construct header with correct checksum if ipv6: header = struct.pack('BbHHh', ICMP_TYPE_IP6, ICMP_CODE, checksum, ICMP_ID, ICMP_SEQ_NR+id) else: header = struct.pack('bbHHh', ICMP_TYPE, ICMP_CODE, checksum, ICMP_ID, ICMP_SEQ_NR+id) # ping packet *with* checksum packet = header + data # a perfectly formatted ICMP echo packet return packet def _in_cksum(packet): """THE RFC792 states: 'The 16 bit one's complement of the one's complement sum of all 16 bit words in the header.' Generates a checksum of a (ICMP) packet. Based on in_chksum found in ping.c on FreeBSD. """ # add byte if not dividable by 2 if len(packet) & 1: packet = packet + '\0' # split into 16-bit word and insert into a binary array words = array.array('h', packet) sum = 0 # perform ones complement arithmetic on 16-bit words for word in words: sum += (word & 0xffff) hi = sum >> 16 lo = sum & 0xffff sum = hi + lo sum = sum + (sum >> 16) return (~sum) & 0xffff # return ones complement def pingNode(alive=0, timeout=1.0, ipv6=0, number=sys.maxint, node=None, flood=0, size=ICMP_DATA_STR): """Pings a node based on input given to the function. """ # if no node, exit if not node: _error("") # if not a valid host, exit if ipv6: if socket.has_ipv6: try: info, port = socket.getaddrinfo(node, None) host = info[4][0] # do not print ipv6 twice if ipv6 address given as node if host == node: noPrintIPv6adr = 1 except: _error("cannot resolve %s: Unknow host" % node) else: _error("No support for IPv6 on this plattform") else: # IPv4 try: host = socket.gethostbyname(node) except: _error("cannot resolve %s: Unknow host" % node) # trying to ping a network? if not ipv6: if int(string.split(host, ".")[-1]) == 0: _error("no support for network ping") # do some sanity check if number == 0: _error("invalid count of packets to transmit: '%s'" % str(a)) if alive: number = 1 # Send the ping(s) start = 1; mint = 999; maxt = 0.0; avg = 0.0 lost = 0; tsum = 0.0; tsumsq = 0.0 # tell the user what we do if not alive: if ipv6: # do not print the ipv6 twice if ip adress given as node # (it can be to long in term window) if noPrintIPv6adr == 1: # add 40 (header) + 8 (icmp header) + payload print "PING %s : %d data bytes (40+8+%d)" % (str(node), 40+8+size, size) else: # add 40 (header) + 8 (icmp header) + payload print "PING %s (%s): %d data bytes (40+8+%d)" % (str(node), str(host), 40+8+size, size) else: # add 20 (header) + 8 (icmp header) + payload print "PING %s (%s): %d data bytes (20+8+%d)" % (str(node), str(host), 20+8+size, size) # trap ctrl-d and ctrl-c try: # send the number of ping packets as given while start <= number: lost += 1 # in case user hit ctrl-c # create the IPv6/IPv4 socket if ipv6: # can not create a raw socket if not root or setuid to root try: pingSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6, socket.SOCK_RAW, socket.getprotobyname("ipv6-icmp")) except socket.error, e: print "socket error: %s" % e _error("You must be root (uses raw sockets)" % os.path.basename(sys.argv[0])) # IPv4 else: # can not create a raw socket if not root or setuid to root try: pingSocket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_RAW, socket.getprotobyname("icmp")) except socket.error, e: print "socket error: %s" % e _error("You must be root (%s uses raw sockets)" % os.path.basename(sys.argv[0])) packet = _construct(start, size, ipv6) # make a ping packet # send the ping try: pingSocket.sendto(packet,(node,1)) except socket.error, e: _error("socket error: %s" % e) # reset values pong = ""; iwtd = [] # wait until there is data in the socket while 1: # input, output, exceptional conditions iwtd, owtd, ewtd = select.select([pingSocket], [], [], timeout) break # no data and timout occurred # data on socket - this means we have an answer if iwtd: # ok, data on socket endtime = time.time() # time packet received # read data (we only need the header) pong, address = pingSocket.recvfrom(size+48) lost -= 1 # in case user hit ctrl-c # examine packet # fetch TTL from IP header if ipv6: # since IPv6 header and any extension header are never passed # to a raw socket, we can *not* get hoplimit field.. # I hoped that a socket option would help, but it's not # supported: # pingSocket.setsockopt(IPPROTO_IPV6, IPV6_RECVHOPLIMIT, 1) # so we can't fetch hoplimit.. # fetch hoplimit #rawPongHop = struct.unpack("c", pong[7])[0] # fetch pong header pongHeader = pong[0:8] pongType, pongCode, pongChksum, pongID, pongSeqnr = \ struct.unpack("bbHHh", pongHeader) # fetch starttime from pong starttime = struct.unpack("d", pong[8:16])[0] # IPv4 else: # time to live rawPongHop = struct.unpack("s", pong[8])[0] # convert TTL from 8 bit to 16 bit integer pongHop = int(binascii.hexlify(str(rawPongHop)), 16) # fetch pong header pongHeader = pong[20:28] pongType, pongCode, pongChksum, pongID, pongSeqnr = \ struct.unpack("bbHHh", pongHeader) # fetch starttime from pong starttime = struct.unpack("d", pong[28:36])[0] # valid ping packet received? if not pongSeqnr == start: pong = None # NO data on socket - timeout waiting for answer if not pong: if alive: print "no reply from %s (%s)" % (str(node), str(host)) else: print "ping timeout: %s (icmp_seq=%d) " % (host, start) # do not wait if just sending one packet if number != 1 and start < number: time.sleep(flood ^ 1) start += 1 continue # lost a packet - try again triptime = endtime - starttime # compute RRT tsum += triptime # triptime for all packets (stddev) tsumsq += triptime * triptime # triptime^2 for all packets (stddev) # compute statistic maxt = max ((triptime, maxt)) mint = min ((triptime, mint)) if alive: print str(node) + " (" + str(host) +") is alive" else: if ipv6: # size + 8 = payload + header print "%d bytes from %s: icmp_seq=%d time=%.5f ms" % \ (size+8, host, pongSeqnr, triptime*1000) else: print "%d bytes from %s: icmp_seq=%d ttl=%s time=%.5f ms" % \ (size+8, host, pongSeqnr, pongHop, triptime*1000) # do not wait if just sending one packet if number != 1 and start < number: # if flood = 1; do not sleep - just ping time.sleep(flood ^ 1) # wait before send new packet # the last thing to do is update the counter - else the value # (can) get wrong when computing summary at the end (if user # hit ctrl-c when pinging) start += 1 # end ping send/recv while # if user ctrl-d or ctrl-c except (EOFError, KeyboardInterrupt): # if user disrupts ping, it is most likly done before # the counter get updates - if do not update it here, the # summary get all wrong. start += 1 pass # compute and print som stats # stddev computation based on ping.c from FreeBSD if start != 0 or lost > 0: # do not print stats if 0 packet sent start -= 1 # since while is '<=' avg = tsum / start # avg round trip vari = tsumsq / start - avg * avg # %-packet lost if start == lost: plost = 100 else: plost = (lost/start)*100 if not alive: print "\n--- %s ping statistics ---" % node print "%d packets transmitted, %d packets received, %d%% packet loss" % \ (start, start-lost, plost) # don't display summary if 100% packet-loss if plost != 100: print "round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = %.3f/%.3f/%.3f/%.3f ms" % \ (mint*1000, (tsum/start)*1000, maxt*1000, math.sqrt(vari)*1000) pingSocket.close() def _error(err): """Exit if running standalone, else raise an exception """ if __name__ == '__main__': print "%s: %s" % (os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]), str(err)) print "Try `%s --help' for more information." % os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]) sys.exit(1) else: raise Exception, str(err) def _usage(): """Print usage if run as a standalone program """ print """usage: %s [OPTIONS] HOST Send ICMP ECHO_REQUEST packets to network hosts. Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too. -c, --count=N Stop after sending (and receiving) 'N' ECHO_RESPONSE packets. -s, --size=S Specify the number of data bytes to be sent. The default is 56, which translates into 64 ICMP data bytes when combined with the 8 bytes of ICMP header data. -f, --flood Flood ping. Outputs packets as fast as they come back. Use with caution! -6, --ipv6 Ping using IPv6. -t, --timeout=s Specify a timeout, in seconds, before a ping packet is considered 'lost'. -h, --help Display this help and exit Report bugs to lars [at] gnist org""" % os.path.basename(sys.argv[0]) if __name__ == '__main__': """Main loop """ # version control version = string.split(string.split(sys.version)[0][:3], ".") if map(int, version) < [2, 3]: _error("You need Python ver 2.3 or higher to run!") try: # opts = arguments recognized, # args = arguments NOT recognized (leftovers) opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:-1], "hat:6c:fs:", ["help", "alive", "timeout=", "ipv6", "count=", "flood", "packetsize="]) except getopt.GetoptError: # print help information and exit: _error("illegal option(s) -- " + str(sys.argv[1:])) # test whether any host given if len(sys.argv) >= 2: node = sys.argv[-1:][0] # host to be pinged if node[0] == '-' or node == '-h' or node == '--help' : _usage() else: _error("No arguments given") if args: _error("illegal option -- %s" % str(args)) # default variables alive = 0; timeout = 1.0; ipv6 = 0; count = sys.maxint; flood = 0; size = ICMP_DATA_STR # run through arguments and set variables for o, a in opts: if o == "-h" or o == "--help": # display help and exit _usage() sys.exit(0) if o == "-t" or o == "--timeout": # timeout before "lost" try: timeout = float(a) except: _error("invalid timout: '%s'" % str(a)) if o == "-6" or o == "--ipv6": # ping ipv6 ipv6 = 1 if o == "-c" or o == "--count": # how many pings? try: count = int(a) except: _error("invalid count of packets to transmit: '%s'" % str(a)) if o == "-f" or o == "--flood": # no delay between ping send flood = 1 if o == "-s" or o == "--packetsize": # set the ping payload size try: size = int(a) except: _error("invalid packet size: '%s'" % str(a)) # just send one packet and say "it's alive" if o == "-a" or o == "--alive": alive = 1 # here we send pingNode(alive=alive, timeout=timeout, ipv6=ipv6, number=count, node=node, flood=flood, size=size) # if we made it this far, do a clean exit sys.exit(0) ### end
Python "pseudo-inplace" file contents
import fileinput for line in file.input('name.txt', inplace=1): print line if line.startswith('something'): pirnt 'xxx' #insert
Python send simple Email
import smtplib def sendEmail(to): fromaddr = 'xx@gmail.com' toaddrs = to #['xxx', 'xxx'] msg = 'test' username = '' password = '' server = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587) server.ehlo() server.starttls() server.login(username, password) server.sendmail(fromaddr, toaddrs, msg) server.quit()
compare "version-style" strings
- use
distutils.version>>> from distutils.version import LooseVersion, StrictVersion >>> LooseVersion("2.3.1") < LooseVersion("10.1.2") True >>> StrictVersion("2.3.1") < StrictVersion("10.1.2") True
- use
tupledef versiontuple(v): return tuple(map(int, (v.split(".")))) >>> versiontuple("2.3.1") > versiontuple("10.1.1") False
- use
reimport re def mycmp(version1, version2): def normalize(v): return [int(x) for x in re.sub(r'(\.0+)*$','', v).split(".")] return cmp(normalize(version1), normalize(version2))
windows install pip
- Install Setup tools. http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#setuptools
- Install PIP http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#setuptools
- Add Python Scripts to the path Start -> Edit environment variables eg. C:\Python27\Scripts
Iterables, Generators and Yield1
Iterables
>>> mylist = [1, 2, 3] >>> for i in mylist: ... print(i) 1 2 3
Generators
Generators are iterators, but you can only iterate over them once. It's because they do not store all the values in memory, they generate the values on the fly:
>>> mygenerator = (x*x for x in range(3)) >>> for i in mygenerator: ... print(i) 0 1 4
BUT, you can not perform for i in mygenerator a second time since generators can only be used once
Yield
Yield is a keyword that is used like return, except the function will
return a generator.
>>> def createGenerator(): ... mylist = range(3) ... for i in mylist: ... yield i*i ... >>> mygenerator = createGenerator() # create a generator >>> print(mygenerator) # mygenerator is an object! <generator object createGenerator at 0xb7555c34> >>> for i in mygenerator: ... print(i) 0 1 4
To master yield, you must understand that when you call the function, the code you have written in the function body does not run. The function only returns the generator object
Now the hard part:
The first time the for calls the generator object created from your
function, it will run the code in your function from the beginning
until it hits yield, then it'll return the first value of the loop.
Then, each other call will run the loop you have written in the
function one more time, and return the next value, until there is no
value to return.
The generator is considered empty once the function runs but does not hit yield anymore. It can be because the loop had come to an end, or because you do not satisfy a "if/else" anymore.
Controlling a generator exhaustion
>>> class Bank(): # let's create a bank, building ATMs ... crisis = False ... def create_atm(self): ... while not self.crisis: ... yield "$100" >>> hsbc = Bank() # when everything's ok the ATM gives you as much as you want >>> corner_street_atm = hsbc.create_atm() >>> print(corner_street_atm.next()) $100 >>> print(corner_street_atm.next()) $100 >>> print([corner_street_atm.next() for cash in range(5)]) ['$100', '$100', '$100', '$100', '$100'] >>> hsbc.crisis = True # crisis is coming, no more money! >>> print(corner_street_atm.next()) <type 'exceptions.StopIteration'> >>> wall_street_atm = hsbc.create_atm() # it's even true for new ATMs >>> print(wall_street_atm.next()) <type 'exceptions.StopIteration'> >>> hsbc.crisis = False # trouble is, even post-crisis the ATM remains empty >>> print(corner_street_atm.next()) <type 'exceptions.StopIteration'> >>> brand_new_atm = hsbc.create_atm() # build a new one to get back in business >>> for cash in brand_new_atm: ... print cash $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 ...
Itertools
>>> import itertools >>> horses = [1, 2, 3, 4] >>> races = itertools.permutations(horses) >>> print(races) <itertools.permutations object at 0xb754f1dc> >>> print(list(itertools.permutations(horses))) [(1, 2, 3, 4), (1, 2, 4, 3), ...]
Understanding the inner mechanisms of iteration
Iteration is a process implying iterables (implementing the __iter__()
method) and iterators (implementing the __next__() method). Iterables
are any objects you can get an iterator from. Iterators are objects
that let you iterate on iterables.
Hidden features of Python2
Obfuscated Python
Interesting obfuscated Python by preshing:
_ =\
"""if!
1:"e,V=100
0,(0j-1)**-.2;
v,S=.5/ V.real,
[(0,0,4 *e,4*e*
V)];w=1 -v"def!
E(T,A, B,C):P
,Q,R=B*w+ A*v,B*w+C
*v,A*w+B*v;retur n[(1,Q,C,A),(1,P
,Q,B),(0,Q,P,A)]*T+[(0,C ,R,B),(1,R,C,A)]*(1-T)"f
or!i!in!_[:11]:S =sum([E (*x)for !x!in!S],[])"imp
ort!cair o!as!O; s=O.Ima geSurfac
e(1,e,e) ;c=O.Con text(s); M,L,G=c.
move_to ,c.line_to,c.s et_sour
ce_rgb a"def!z(f,a) :f(-a.
imag,a. real-e-e)"for!T,A,B,C!in[i !for!i!
in!S!if!i[""";exec(reduce(lambda x,i:x.replace(chr
(i),"\n "[34-i:]), range( 35),_+"""0]]:z(M,A
);z(L,B);z (L,C); c.close_pa
th()"G (.4,.3 ,1);c.
paint( );G(.7 ,.7,1)
;c.fil l()"fo r!i!in
!range (9):"! g=1-i/
8;d=i/ 4*g;G(d,d,d, 1-g*.8
)"!def !y(f,a):z(f,a+(1+2j)*( 1j**(i
/2.))*g)"!for!T,A,B,C!in!S:y(M,C);y(L,A);y(M
,A);y(L,B)"!c.st roke()"s.write_t
o_png('pen rose.png')
""" ))
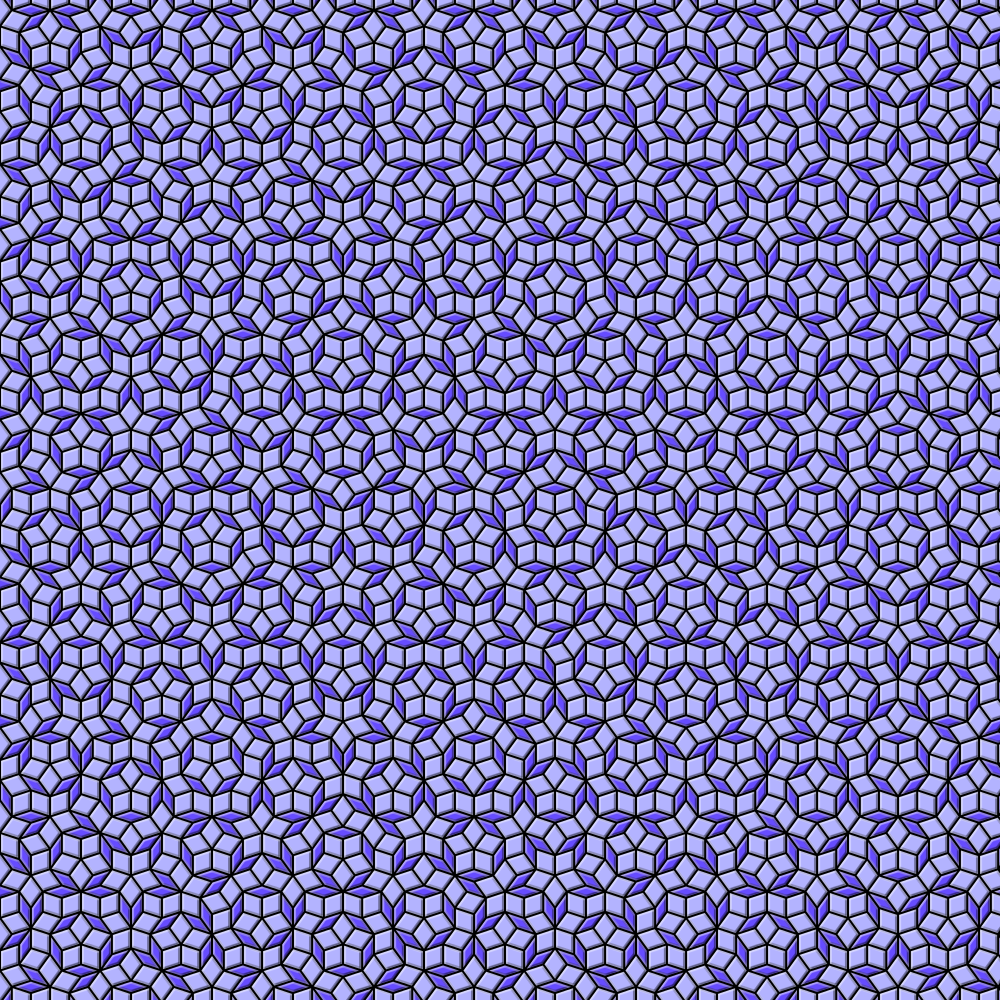
_ = (
255,
lambda
V ,B,c
:c and Y(V*V+B,B, c
-1)if(abs(V)<6)else
( 2+c-4*abs(V)**-0.4)/i
) ;v, x=1500,1000;C=range(v*x
);import struct;P=struct.pack;M,\
j ='<QIIHHHH',open('M.bmp','wb').write
for X in j('BM'+P(M,v*x*3+26,26,12,v,x,1,24))or C:
i ,Y=_;j(P('BBB',*(lambda T:(T*80+T**9
*i-950*T **99,T*70-880*T**18+701*
T **9 ,T*i**(1-T**45*2)))(sum(
[ Y(0,(A%3/3.+X%v+(X/v+
A/3/3.-x/2)/1j)*2.5
/x -2.7,i)**2 for \
A in C
[:9]])
/9)
) )
isinstance() vs type()3
- isinstance caters for inheritance (an instance of a derived class is an instance of a base class, too),
- while checking for equality of type does not (it demands identity of types and rejects instances of subtypes, AKA subclasses).