Linux logging
Table of Contents
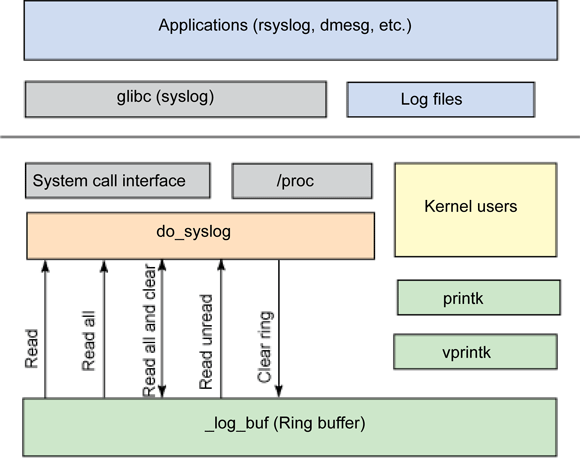
Overview
syslog(application) uses Unix Domain Socket
- server
struct sockaddr_un ipcFile; memset(&ipcFile, 0, sizeof(ipcFile)); ipcFile.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strcpy(ipcFile.sun_path, filename.c_str()); int socket = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); bind(socket, (struct sockaddr *) &ipcFile, sizeof(ipcFile)); ... // buf contains the data, buflen contains the number of bytes int bytes = write(socket, buf, buflen); ... close(socket); unlink(ipcFile.sun_path);
- client
With datagram sockets, specifically unix domain datagram sockets,
the client has to
bind()to its own endpoint, thenconnect()to the server's endpoint.
char * server_filename = "/tmp/socket-server"; char * client_filename = "/tmp/socket-client"; struct sockaddr_un server_addr; struct sockaddr_un client_addr; memset(&server_addr, 0, sizeof(server_addr)); server_addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strncpy(server_addr.sun_path, server_filename, 104); // XXX: should be limited to about 104 characters, system dependent memset(&client_addr, 0, sizeof(client_addr)); client_addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX; strncpy(client_addr.sun_path, client_filename, 104); // get socket int sockfd = socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); // bind client to client_filename bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &client_addr, sizeof(client_addr)); // connect client to server_filename connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr)); ... char buf[1024]; int bytes = read(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf)); ... close(sockfd);
maximum of size of a packet that can be sent on a Unix socket
- The
wmem_maxsocket send buffer maximum size kernel setting, which determines the maximum size of the send buffer that can be set usingsetsockopt (SO_SNDBUF). The current setting can be read from/proc/sys/net/core/wmem_maxand can be set usingsysctl net.core.wmem_max=VALUE(add the setting to/etc/sysctl.confto make the change persistent across reboots). Note this setting applies to all sockets and socket protocols, not just to Unix sockets. - If multiple packets are sent to a Unix socket (using
SOCK_DATAGRAM), then the maximum amount of data which can be sent without blocking depends on both the size of the socket send buffer (see above) and the maximum number of unread packets on the Unix socket (kernel parameternet.unix.max_dgram_qlen). - A packet (
SOCK_DATAGRAM) requires contiguous memory. How much contiguous memory is available in the kernel will depend on many factors (e.g. the I/O load on the system, etc…).
the practical limits will be around wmem_max ~8Mb and
unix_dgram_qlen ~32.