OpenWrt Boot Process (New OpenWrt)
Table of Contents
一个boot log的例子:
[ 2.602573] VFS: Mounted root (squashfs filesystem) readonly on device 31:2.
[ 2.610535] Freeing unused kernel memory: 224K (80428000 - 80460000)
[ 3.912151] init: Console is alive
[ 3.916056] init: - watchdog -
[ 6.994992] init: - preinit -
Press the [f] key and hit [enter] to enter failsafe mode
Press the [1], [2], [3] or [4] key and hit [enter] to select the debug level
Before mount_root
[ 10.352510] jffs2: notice: (401) jffs2_build_xattr_subsystem: complete building xattr subsystem, 0 of xdatum (0 unchecked, 0 orphan) and 0 of xref (0 dead, 0 orphan) found.
[ 10.369525] mount_root: switching to jffs2 overlay
[ 10.540372] procd: - early -
[ 10.543495] procd: - watchdog -
[ 11.303217] procd: - ubus -
[ 12.307928] random: ubusd: uninitialized urandom read (4 bytes read, 53 bits of entropy available)
[ 12.439119] procd: - init -
Please press Enter to activate this console.
Overview
- Boot
- Bootloader 比如U-Boot, 配置底层硬件,加载Linux kernel 和 device tree blob, 最后传入kernel cmdline跳转到Linux kernel image.
- 高通的Secure boot会复杂点,先PBL(Primary Boot Loader), 然后 SBL1(Second BootLoader stage 1) 初始化buses、DDR、clocks等, SBL1 移交运行控制权给QSEE。QSEE建立安全运行环境,配置xPU,支持fuse, 之后才转入APPSBL即为BootLoader, 跳转到HLOS(High LevelOperating System) 即为Linux kernel.
- Kernel init Hareware
Linux Kernel 将继续初始化外围硬件.
- Kernel -> Filesystem
Mount the root filesystem (通过kernel cmdline中的诸如参数
root=,rootfstype=). - Kernel -> Init Process
最后kernel启动
init进程 (PID 1). - Run preinit
再procd接管前, preinit会对系统做一些前期的初始工作.
- Run procd
一旦preinit完成,它将exec procd. 这将用procd取代原来pid1的init进程. watchdog的file descriptor不会被关闭, 而是传入到procd进程.
OpenWrt系统从第4步开始. 在OpenWrt系统中, 这个init初始化进程不是普通 Linux中一个初始进程, 而是专为OpenWrt写的一个shell脚本.
preinit
/etc/preinit
无论Linux什么版本, OpenWrt都会有类似如下的patch,把OpenWrt的init进程放在第一个位置:
--- a/init/main.c +++ b/init/main.c @@ -963,7 +963,8 @@ static int __ref kernel_init(void *unuse pr_err("Failed to execute %s (error %d). Attempting defaults...\n", execute_command, ret); } - if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") || + if (!try_to_run_init_process("/etc/preinit") || + !try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") || !try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh"))
/etc/preinit 如下:
#!/bin/sh # Copyright (C) 2006 OpenWrt.org # Copyright (C) 2010 Vertical Communications [ -z "$PREINIT" ] && exec /sbin/init export PATH=/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin pi_ifname= pi_ip=192.168.1.1 pi_broadcast=192.168.1.255 pi_netmask=255.255.255.0 fs_failsafe_ifname= fs_failsafe_ip=192.168.1.1 fs_failsafe_broadcast=192.168.1.255 fs_failsafe_netmask=255.255.255.0 fs_failsafe_wait_timeout=0 pi_suppress_stderr="y" pi_init_suppress_stderr="y" pi_init_path="/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" pi_init_cmd="/sbin/init" . /lib/functions.sh . /lib/functions/preinit.sh . /lib/functions/system.sh boot_hook_init preinit_essential boot_hook_init preinit_main boot_hook_init failsafe boot_hook_init initramfs boot_hook_init preinit_mount_root for pi_source_file in /lib/preinit/*; do . $pi_source_file done boot_run_hook preinit_essential pi_mount_skip_next=false pi_jffs2_mount_success=false pi_failsafe_net_message=false boot_run_hook preinit_main
这里第一行命令是:
[ -z "$PREINIT" ] && exec /sbin/init
PREINIT 还没有define, 所以执行 /sbin/init. 这个程序来自package
procd.
/sbin/init
package procd中 init.c 的main函数基本流程如下:1
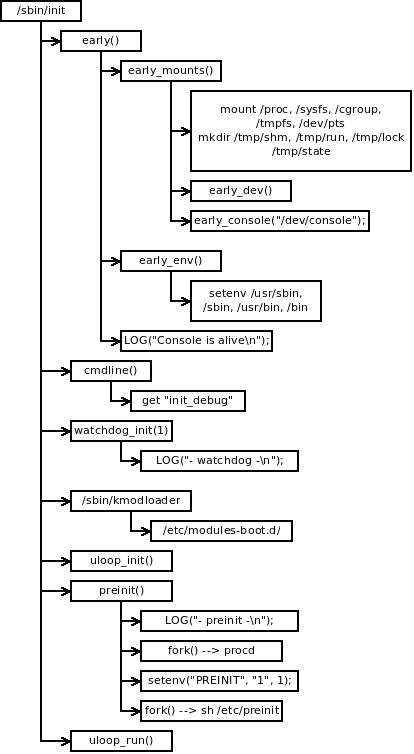
early()early_mounts(): mount /proc /sys/{,fs/cgroup} /dev/{,shm,pts} 等;early_console(): 初始化/dev/console;early_env();: PATH 配置成/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin;- 打印出最上面bootlog实例中的一个message "Console is alive";
cmdline():get_cmdline_val("init_debug", line, sizeof(line));从/proc/cmdline中读取kernel boot commands,并解析出init_debug的值watchdog_init(1): 先从env的WDTFD中获取watchdog的fd,若不存在, 就尝试打开/dev/watchdog. 并初始化watchdog, 最后打印出最上面 bootlog实例中的message "- watchdog -"fork一个新的进程来让/sbin/kmodloader从/etc/modules-boot.d/加载device drivers (注意,这里加载的是boot期间的drivers而不是/etc/modules.d/)uloop_init()初始化uloop (event loop implementation, 来自package libubox). 之后procd和sh /etc/preinit将由uloop管理;preinit()- 打印最上面的第三条信息 "- preinit -"
- fork一个新的进程执行
/sbin/procd -h /etc/hotplug-preinit.json, 并在完后执行一个callback functionplugd_proc_cb(仅仅做了proc->pid = 0;) setenv("PREINIT", "1", 1);- fork一个新的进程执行
sh /etc/preinit, 并在完后执行一个callback functionspawn_procd,spawn_procd将wdtfd设置到env中的WDTFD, 从/tmp/debuglevel读取的 debug level设置到env中的DBGLVL. 最后 fork一个新进程执行/sbin/procd
uloop_run(): 最后由uloop接管
再次执行 /etc/preinit
init进程再次执行 /etc/preinit, 第一部分如下:
export PATH=/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin pi_ifname= pi_ip=192.168.1.1 pi_broadcast=192.168.1.255 pi_netmask=255.255.255.0 fs_failsafe_ifname= fs_failsafe_ip=192.168.1.1 fs_failsafe_broadcast=192.168.1.255 fs_failsafe_netmask=255.255.255.0 fs_failsafe_wait_timeout=0 pi_suppress_stderr="y" pi_init_suppress_stderr="y" pi_init_path="/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" pi_init_cmd="/sbin/init"
如上仅仅定义些变量.
从如下地方定义一些函数:
. /lib/functions.sh . /lib/functions/preinit.sh . /lib/functions/system.sh
定义在 /lib/functions/preinit.sh 中的 boot_hook_init 被用来初始化如下hook
boot_hook_init preinit_essential boot_hook_init preinit_main boot_hook_init failsafe boot_hook_init initramfs boot_hook_init preinit_mount_root
/lib/preinit/ 下的脚本都被执行. 这些脚本主要通过 boot_hook_add 来添加各个hook函数
for pi_source_file in /lib/preinit/*; do . $pi_source_file done
最后分别执行 preinit_essential 和 preinit_main 中的hook函数.
boot_run_hook preinit_essential boot_run_hook preinit_main
procd
OpenWrt使用 procd 来启动系统,管理进程和处理部分kernel与用户层的交互.
procd 首先做一些初始化工作, setsid(); 设置自己成为进程组的所有者,
uloop_init(); 为后续 uloop_run 做初始化, procd_signal(); 设置好
signals.
void procd_signal(void)
{
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
if (getpid() != 1)
return;
sigaction(SIGTERM, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGINT, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGUSR1, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGUSR2, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &sa_crash, NULL);
sigaction(SIGBUS, &sa_crash, NULL);
sigaction(SIGHUP, &sa_dummy, NULL);
sigaction(SIGKILL, &sa_dummy, NULL);
sigaction(SIGSTOP, &sa_dummy, NULL);
reboot(RB_DISABLE_CAD);
}
procd 共有6个状态, STATE_EARLY, STATE_UBUS, STATE_INIT,
STATE_RUNNING, STATE_SHUTDOWN 和 STATE_HALT, procd 的状态从第一个直到最后一个.
static void state_enter(void) { char ubus_cmd[] = "/sbin/ubusd"; switch (state) { case STATE_EARLY: LOG("- early -\n"); watchdog_init(0); hotplug("/etc/hotplug.json"); procd_coldplug(); break; case STATE_UBUS: // try to reopen incase the wdt was not available before coldplug watchdog_init(0); set_stdio("console"); LOG("- ubus -\n"); procd_connect_ubus(); service_init(); service_start_early("ubus", ubus_cmd); break; case STATE_INIT: LOG("- init -\n"); procd_inittab(); procd_inittab_run("respawn"); procd_inittab_run("askconsole"); procd_inittab_run("askfirst"); procd_inittab_run("sysinit"); // switch to syslog log channel ulog_open(ULOG_SYSLOG, LOG_DAEMON, "procd"); break; case STATE_RUNNING: LOG("- init complete -\n"); break; case STATE_SHUTDOWN: /* Redirect output to the console for the users' benefit */ set_console(); LOG("- shutdown -\n"); procd_inittab_run("shutdown"); sync(); break; case STATE_HALT: // To prevent killed processes from interrupting the sleep signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN); LOG("- SIGTERM processes -\n"); kill(-1, SIGTERM); sync(); sleep(1); LOG("- SIGKILL processes -\n"); kill(-1, SIGKILL); sync(); sleep(1); if (reboot_event == RB_POWER_OFF) LOG("- power down -\n"); else LOG("- reboot -\n"); /* Allow time for last message to reach serial console, etc */ sleep(1); /* We have to fork here, since the kernel calls do_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS) * in linux/kernel/sys.c, which can cause the machine to panic when * the init process exits... */ if (!vfork( )) { /* child */ reboot(reboot_event); _exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } while (1) sleep(1); break; default: ERROR("Unhandled state %d\n", state); return; }; }
STATE_EARLY
watchdog_init(0);初始化watchdog;hotplug("/etc/hotplug.json");将根据/etc/hotplug.json中定义的规则来监视hotplug event;procd_coldplug();重新mount/dev, fork新进程来运行udevtrigger, 它将产生coldplug events来让hotplug监视;- 当
=udevtrigger完成, callback函数udevtrigger_complete中最后将调用procd_state_next()来使得状态从STATE_EARLY到STATE_UBUS.;
static void coldplug_complete(struct uloop_timeout *t) { DEBUG(4, "Coldplug complete\n"); hotplug_last_event(NULL); procd_state_next(); }
STATE_UBUS
watchdog_init(0);再次初始化watchdog, 防止在coldplug之前watchdog不可用;set_stdio("console");设置stdin/out/err 到/dev/console;procd_connect_ubus();定义一个定时器不断去connectubusd即使这里ubusd还没创建好. 当procd之后连上ubusd, 它将注册services,main_objec,system_object和watch_event.;ubus_connect(ubus_socket);这里用的是/var/run/ubus.sock(UBUS_UNIX_SOCKET), 连上ubus后,procd_state_ubus_connect()进入STATE_INIT;service_init();为之后services和validators的管理初始化ALV tree;service_start_early("ubus", ubus_cmd);开始ubusd后台服务;
static void ubus_connect_cb(struct uloop_timeout *timeout) { ctx = ubus_connect(ubus_socket); if (!ctx) { DEBUG(4, "Connection to ubus failed\n"); uloop_timeout_set(&ubus_timer, 1000); return; } ctx->connection_lost = ubus_disconnect_cb; ubus_init_service(ctx); ubus_init_system(ctx); watch_ubus(ctx); DEBUG(2, "Connected to ubus, id=%08x\n", ctx->local_id); ubus_add_uloop(ctx); procd_state_ubus_connect(); }
STATE_INIT
根据 handlers[] 中定义, procd在inittab中支持5个命令:
- respawn - this works just like you expect it. It starts a process and will respawn it once it has completed.
- respawnlate - this works like the respawn but will start the process only when the procd init is completed.
- askfirst - this works just like respawn but will print the line “Please press Enter to activate this console.” before starting the process
- askconsole - this works like askfirst but, instead of running on the
tty passed as a parameter, it will look for the tty defined in the
kernel command line using
“console=” - askconsolelate - this works like the askconsole but will start the process only when the procd init is completed.
- sysinit - this will trigger procd to run the command, given as a
parameter, only once. This is usually used to trigger execution of
/etc/rc.d/ procd_inittab();读取/etc/inittab, 初始化actions表procd_inittab_run依次runprocd_inittab_run("respawn"); procd_inittab_run("askconsole"); procd_inittab_run("askfirst"); procd_inittab_run("sysinit")
procd_inittab_run会与/etc/inittab创建的actions表对比, 只运行其中定义的askconsole–>askfirst()和sysinit–>runrc()
#/etc/inittab ::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS S boot ::shutdown:/etc/init.d/rcS K shutdown ::askconsole:/bin/ash --login
static struct init_handler handlers[] = { { .name = "sysinit", .cb = runrc, }, { .name = "shutdown", .cb = runrc, }, { .name = "askfirst", .cb = askfirst, .multi = 1, }, { .name = "askconsole", .cb = askconsole, .multi = 1, }, { .name = "respawn", .cb = rcrespawn, .multi = 1, } };
static char *ask = "/sbin/askfirst"; static void askconsole(struct init_action *a) { char line[256], *tty, *split; int i; tty = get_cmdline_val("console", line, sizeof(line)); if (tty != NULL) { split = strchr(tty, ','); if (split != NULL) *split = '\0'; if (!dev_exist(tty)) { DEBUG(4, "skipping %s\n", tty); return; } console = strdup(tty); a->id = strdup(tty); } else { console = NULL; a->id = NULL; } a->tout.cb = respawn; for (i = MAX_ARGS - 1; i >= 1; i--) a->argv[i] = a->argv[i - 1]; a->argv[0] = ask; a->respawn = 500; a->proc.cb = child_exit; fork_worker(a); }
static void runrc(struct init_action *a) { if (!a->argv[1] || !a->argv[2]) { ERROR("valid format is rcS <S|K> <param>\n"); return; } /* proceed even if no init or shutdown scripts run */ if (rcS(a->argv[1], a->argv[2], rcdone)) rcdone(NULL); }
STATE_RUNNING
基本的系统起来了, procd在 uloop_run() 中执行, 开始管理daemons和
services.
Reference
procd/initd/init.c
int main(int argc, char **argv) { pid_t pid; ulog_open(ULOG_KMSG, LOG_DAEMON, "init"); sigaction(SIGTERM, &sa_shutdown, NULL); sigaction(SIGUSR1, &sa_shutdown, NULL); sigaction(SIGUSR2, &sa_shutdown, NULL); early(); cmdline(); watchdog_init(1); pid = fork(); if (!pid) { char *kmod[] = { "/sbin/kmodloader", "/etc/modules-boot.d/", NULL }; if (debug < 3) { int fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR); if (fd > -1) { dup2(fd, STDIN_FILENO); dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO); dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO); if (fd > STDERR_FILENO) close(fd); } } execvp(kmod[0], kmod); ERROR("Failed to start kmodloader\n"); exit(-1); } if (pid <= 0) { ERROR("Failed to start kmodloader instance\n"); } else { int i; for (i = 0; i < 120; i++) { if (waitpid(pid, NULL, WNOHANG) > 0) break; sleep(1); watchdog_ping(); } } uloop_init(); preinit(); uloop_run(); return 0; }
struct init_handler handlers[]
static struct init_handler handlers[] = { { .name = "sysinit", .cb = runrc, }, { .name = "shutdown", .cb = runrc, }, { .name = "askfirst", .cb = askfirst, .multi = 1, }, { .name = "askconsole", .cb = askconsole, .multi = 1, }, { .name = "respawn", .cb = rcrespawn, .multi = 1, } };
int rcS(char *pattern, char *param, void (*q_empty)(struct runqueue *)) { runqueue_init(&q); q.empty_cb = q_empty; q.max_running_tasks = 1; return _rc(&q, "/etc/rc.d", pattern, "*", param); } static int _rc(struct runqueue *q, char *path, const char *file, char *pattern, char *param) { char *dir = alloca(2 + strlen(path) + strlen(file) + strlen(pattern)); glob_t gl; int j; if (!dir) { ERROR("Out of memory in %s.\n", file); return -1; } DEBUG(2, "running %s/%s%s %s\n", path, file, pattern, param); sprintf(dir, "%s/%s%s", path, file, pattern); if (glob(dir, GLOB_NOESCAPE | GLOB_MARK, NULL, &gl)) { DEBUG(2, "glob failed on %s\n", dir); return -1; } for (j = 0; j < gl.gl_pathc; j++) add_initd(q, gl.gl_pathv[j], param); globfree(&gl); return 0; }
static void rcdone(struct runqueue *q) { procd_state_next(); }