Segment Tree
Table of Contents
Overview
Segment Tree is a data structure that allows efficient (ie, the asymptotic behavior \(O(log n)\) to implement the operation of the form: find the amount / minimum of the array of elements in a given interval (a[l..r] where land rare input to the algorithm), thus further possible to change the elements of the array: as a change in the value of one item, and change elements on a whole array of subsegments (ie, allowed to assign all the elements of a [l…r] any value or add to all the elements of the array any number).
- An important feature of the segments of trees is that they consume a linear memory capacity.
- Leaf Nodes are the elements of the input array.
- Each internal node represents some merging of the leaf nodes. The merging may be different for different problems.
- For each node at index i, the left child is at index 2*i+1, right child at 2*i+2 and the parent is at (i-1)/2.
A example of sum:
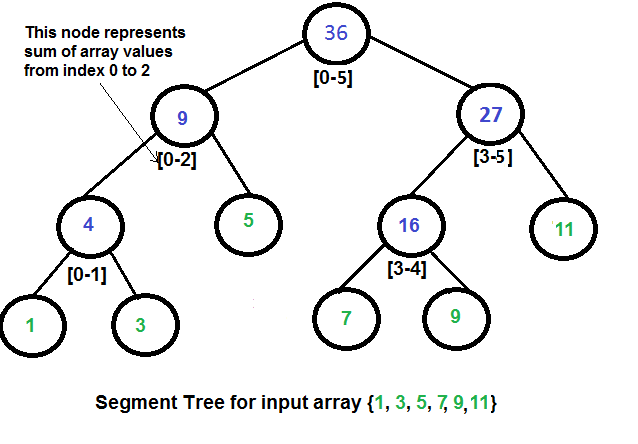
Segment Tree(Sum of given range)1
// C program to show segment tree operations like construction, query // and update #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> // A utility function to get the middle index from corner indexes. int getMid(int s, int e) { return s + (e -s)/2; } /* A recursive function to get the sum of values in given range of the array. The following are parameters for this function. st --> Pointer to segment tree si --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially 0 is passed as root is always at index 0 ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented by current node, i.e., st[si] qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range */ int getSumUtil(int *st, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int si) { // If segment of this node is a part of given range, then return // the sum of the segment if (qs <= ss && qe >= se) return st[si]; // If segment of this node is outside the given range if (se < qs || ss > qe) return 0; // If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range int mid = getMid(ss, se); return getSumUtil(st, ss, mid, qs, qe, 2*si+1) + getSumUtil(st, mid+1, se, qs, qe, 2*si+2); } /* A recursive function to update the nodes which have the given index in their range. The following are parameters st, si, ss and se are same as getSumUtil() i --> index of the element to be updated. This index is in input array. diff --> Value to be added to all nodes which have i in range */ void updateValueUtil(int *st, int ss, int se, int i, int diff, int si) { // Base Case: If the input index lies outside the range of // this segment if (i < ss || i > se) return; // If the input index is in range of this node, then update // the value of the node and its children st[si] = st[si] + diff; if (se != ss) { int mid = getMid(ss, se); updateValueUtil(st, ss, mid, i, diff, 2*si + 1); updateValueUtil(st, mid+1, se, i, diff, 2*si + 2); } } // The function to update a value in input array and segment tree. // It uses updateValueUtil() to update the value in segment tree void updateValue(int arr[], int *st, int n, int i, int new_val) { // Check for erroneous input index if (i < 0 || i > n-1) { printf("Invalid Input"); return; } // Get the difference between new value and old value int diff = new_val - arr[i]; // Update the value in array arr[i] = new_val; // Update the values of nodes in segment tree updateValueUtil(st, 0, n-1, i, diff, 0); } // Return sum of elements in range from index qs (quey start) // to qe (query end). It mainly uses getSumUtil() int getSum(int *st, int n, int qs, int qe) { // Check for erroneous input values if (qs < 0 || qe > n-1 || qs > qe) { printf("Invalid Input"); return -1; } return getSumUtil(st, 0, n-1, qs, qe, 0); } // A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for array[ss..se]. // si is index of current node in segment tree st int constructSTUtil(int arr[], int ss, int se, int *st, int si) { // If there is one element in array, store it in current node of // segment tree and return if (ss == se) { st[si] = arr[ss]; return arr[ss]; } // If there are more than one elements, then recur for left and // right subtrees and store the sum of values in this node int mid = getMid(ss, se); st[si] = constructSTUtil(arr, ss, mid, st, si*2+1) + constructSTUtil(arr, mid+1, se, st, si*2+2); return st[si]; } /* Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to fill the allocated memory */ int *constructST(int arr[], int n) { // Allocate memory for segment tree //Height of segment tree int x = (int)(ceil(log2(n))); //Maximum size of segment tree int max_size = 2*(int)pow(2, x) - 1; // Allocate memory int *st = new int[max_size]; // Fill the allocated memory st constructSTUtil(arr, 0, n-1, st, 0); // Return the constructed segment tree return st; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { int arr[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11}; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); // Build segment tree from given array int *st = constructST(arr, n); // Print sum of values in array from index 1 to 3 printf("Sum of values in given range = %d\n", getSum(st, n, 1, 3)); // Update: set arr[1] = 10 and update corresponding // segment tree nodes updateValue(arr, st, n, 1, 10); // Find sum after the value is updated printf("Updated sum of values in given range = %d\n", getSum(st, n, 1, 3)); return 0; }
Lazy propagation
再更新一段数据时,利用lazy propagation,可以做到 \(O(logn)\)
节点数据向上更新
将子节点的值更新到父节点。
/* 对于区间求和 */ void push_up(int rt) { tree[rt] = tree[rt << 1] + tree[rt << 1 | 1]; } /* 对于区间求最大值 */ void push_up(int rt) { tree[rt] = max(tree[rt << 1], tree[rt << 1 | 1]); }
节点懒惰标记下推
对于区间求和, 原子数组值需要加上lazy标记乘以子树所统计的区间长度。 len 为父节点统计的区间长度, 则len - (len >> 1)为左子树区间长度, len >> 1为右子树区间长度。
void push_down(int rt, int len) { tree[rt << 1] += lazy[rt] * (len - (len >> 1)); lazy[rt << 1] += lazy[rt]; tree[rt << 1 | 1] += lazy[rt] * (len >> 1); lazy[rt << 1 | 1] += lazy[rt]; lazy[rt] = 0; }
对于区间求最大值, 子树的值不需要乘以长度, 所以不需要传递参数len。
void push_down(int rt) { tree[rt << 1] += lazy[rt]; lazy[rt << 1] += lazy[rt]; tree[rt << 1 | 1] += lazy[rt]; lazy[rt << 1 | 1] += lazy[rt]; lazy[rt] = 0; }
建树
新建一棵长度N的线段树。
#define lchild rt << 1, l, m #define rchild rt << 1 | 1, m + 1, r void build(int rt = 1, int l = 1, int r = N) { if (l == r) { std::cin >> tree[rt]; return; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(lchild); build(rchild); push_up(rt); }
更新
单点更新, 不需要用到lazy标记
#define lchild rt << 1, l, m #define rchild rt << 1 | 1, m + 1, r void update(int p, int delta, int rt = 1, int l = 1, int r = N) { if (l == r) { tree[rt] += delta; return; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; if (p <= m) update(p, delta, lchild); else update(p, delta, rchild); push_up(rt); }
成段更新, 需要用到lazy标记来提高时间效率
#define lchild rt << 1, l, m #define rchild rt << 1 | 1, m + 1, r void update(int L, int R, int delta, int rt = 1, int l = 1, int r = N) { if (L <= l && r <= R) { tree[rt] += delta * (r - l + 1); lazy[rt] += delta; return; } if (lazy[rt]) push_down(rt, r - l + 1); int m = (l + r) >> 1; if (L <= m) update(L, R, delta, lchild); if (R > m) update(L, R, delta, rchild); push_up(rt); }
区间查询
#define lchild rt << 1, l, m #define rchild rt << 1 | 1, m + 1, r int query(int L, int R, int rt = 1, int l = 1, int r = N) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return tree[rt]; if (lazy[rt]) push_down(rt, r - l + 1); int m = (l + r) >> 1, ret = 0; if (L <= m) ret += query(L, R, lchild); if (R > m) ret += query(L, R, rchild); return ret; }
More
- Segment Tree(Range Minimum Query): http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/segment-tree-set-1-range-minimum-query/
- segment trees basic explanation and examples: http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/18051 and http://e-maxx.ru/algo/segment_tree
- more solution with segment trees: http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/15890 and http://letuskode.blogspot.hk/2013/01/segtrees.html